Pinjar(ピンジャー)
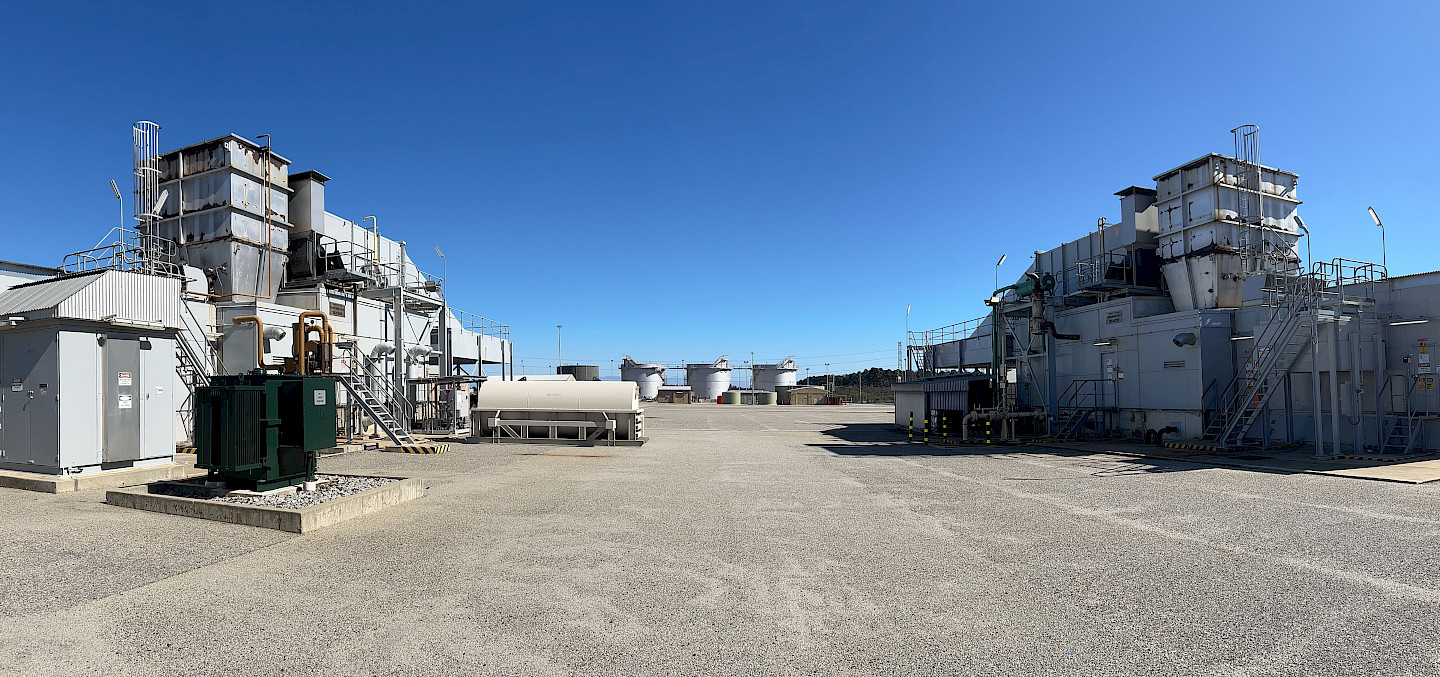

ピンジャーには、SSSクラッチを搭載した6基のFrame 6ガスタービン発電所があります(新設3基、レトロフィット3基)。これらは、西オーストラリア州の電力系統の安定化を支援するため、同期コンデンサーとして運転可能です。
シナジー社が所有するピンジャー発電所は、パースの北約50マイルに位置しており、西オーストラリア州のこの地域および南西相互接続系統(SWIS)ネットワークにとって重要なバックアップ電源を提供しています。この発電所には、6基のFrame 6ガスタービンと3基のFrame 9ガスタービンが設置されています。これらのガスタービンは、夏の最も暑い日などのピーク需要時、緊急時、および定期試験時に電力を供給するために運転されます。
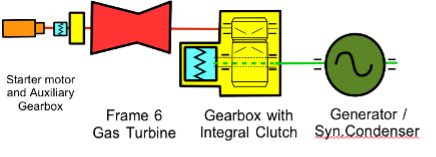
Frame 6ユニットは1989年に初めて運転を開始しました。元のユニットのうち3基にはSSSクラッチが装着されており、通常の発電を行っていないときでも、地域の無効電力需要を支援するために同期コンデンサーとして運転できるようになっています。
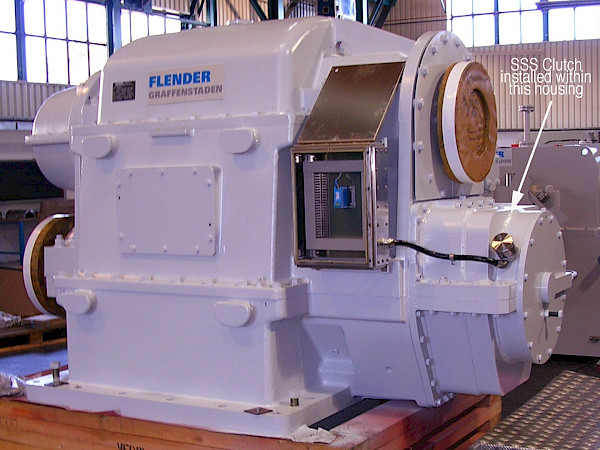
2006年に、残りの3基のユニットも同期コンデンサーとして運転できるように改造されました。これは、既存のフレンダー・グラッフェンシュターデン製減速ギアボックスを交換することで容易に実現されました。新しいギアボックスには、それぞれ194TのSSSクラッチがクイルシャフト方式で組み込まれています。これにより、ガスタービンや発電機を移動させることなくSSSクラッチを追加することが可能となりました。

このサイトで非常に興味深いのは、プラントのニーズが年々どのように変化してきたか、そしてSSSクラッチの導入が、運転者だけでなく地域の電力系統に対しても発電の柔軟性を提供している点です。
1990年代には、同期コンデンサー運転モードにより、遠隔地まで長い送電線を持つ地域の無効電力を支援することが可能でした。現在、西オーストラリア州では大量の太陽光発電が導入され、古い石炭火力発電所の運転停止が進んでいます。最近のAEMOによる西オーストラリア電力市場に関する報告書では、以下の課題が指摘され、発電所の閉鎖前に必要なサービスを確保することが約束されています。
石炭火力およびガス火力(熱電併給)発電の閉鎖と、インバーター接続型再生可能エネルギーの導入増加が重なることで、SWISにおける短絡電流、動的無効電力支援、そして慣性が減少すると予測されています。これを適切に管理しない場合、電力系統の保護装置の有効性が低下し、電力系統の安定性や信頼性にリスクをもたらす可能性があります。
ピンジャーのハイブリッド構成は、この新しい環境での運転に非常に適しており、SSSクラッチによって可能となるピーク需要対応の発電と電力系統安定化サービスの両方を提供します。

西オーストラリアにおけるダックカーブ対策 - MPS (PDF)
太陽光発電ピーク時の安定供給を支えるピンジャー発電所の取り組み